Real Estate Finance
The real estate securitization is a scheme in which the property is transformed into the security and is widely sold to investors. In the Japanese real estate securitization, it is common to use a special purpose company (“SPC”), such as Godo Kaisha(“GK”), Tokutei Mokuteki Kaisha (“TMK”) or real investment trust (“REIT”), to securitize cash-generating assets; for example, offices, residential and retail properties, distribution centers and hotels.
The key objectives and benefits of real estate securitization include the followings.
- ・The originator, who possesses the underlying assets, not only is able to remove them from the balance sheet but also is able to improve the financial position by repaying the existing debt as the sales proceeds.
- ・The investors are able to invest in the properties as small amount by investing in SPCs.
SMBC provides a non-recourse loan in the real estate securitization structure.
The non-recourse loan is a type of a secured loan of which repayment sources are limited to the cash flows generated from the underlying properties. A typical structure in Japan is as bellow.
Typical structure of non-recourse loan
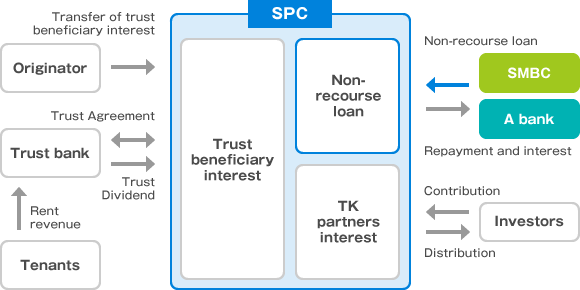
(Note) The SPC is generally incorporated as “Toshi Hojin” (i.e. an investment corporation) under the specific Japanese law.
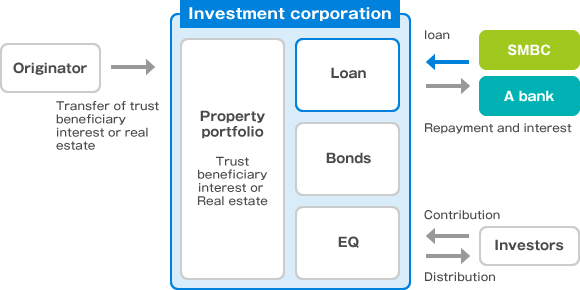
For example, in a case which the SPC is an investment corporation, or REIT, the debt services to the banks are made out of the cash flows originally from its portfolio (e.g. rents).
Typical structure of loan to J-REIT
In the Japanese real estate securitization scheme, SMBC has long played multiple roles including arranging and agenting in addition to lending. We also support our customers in building up the Corporate Real Estate (“CRE”) strategy to maximize their corporate value-adds in terms of real estate, enhance their balance sheets and plan for the future corporate strategy.